Accounting Ratios Overview, Examples, Formulas

Refer to the chart of accounts illustrated in the previous section. The basic accounting formula only relates to the double entry bookkeeping system, where all entries made are intended to balance using this formula. If a business is using a single entry system, the formula does not apply. Shareholder Equity is equal to a business’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It can be found on a balance sheet and is one of the most important metrics for analysts to assess the financial health of a company. Liabilities are considered to be anything that is a claim against the company’s assets, such as accounts payable or other debts that the company owes.
Quick Ratio Formula With Examples, Pros and Cons – Investopedia
Quick Ratio Formula With Examples, Pros and Cons.
Posted: Tue, 31 Oct 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
However, due to the fact that accounting is kept on a historical basis, the equity is typically not the net worth of the organization. Often, a company may depreciate capital assets in 5–7 years, meaning that the assets will show on the books as less than their “real” value, or what they would be worth on the secondary accounting formula market. The accounting equation is fundamental to the double-entry bookkeeping practice. In other words, the total amount of all assets will always equal the sum of liabilities and shareholders’ equity. The accounting equation is a concise expression of the complex, expanded, and multi-item display of a balance sheet.
Example of Accounting Formula (With Excel Template)
This could be due to poor training, hiring less experienced personnel, or problematic production equipment. To calculate the material yield variance, subtract the standard unit usage from actual unit usage, and multiply by the standard cost per unit. If the variance is unfavorable, there may be an excessive amount of scrap in the production process or spoilage in the warehouse, or a lower quality of materials being acquired. To calculate the selling price variance, subtract the budgeted price from the actual price, and multiply by the actual unit sales. If the variance is unfavorable, it means the actual selling price was lower than the standard selling price. This may indicate an excessive usage of sales discounts or other promotions.
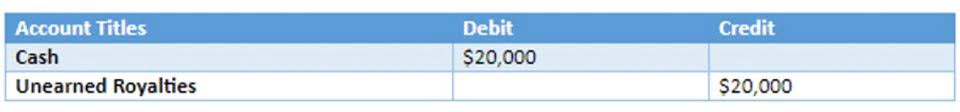
These equations, entered in a business’s general ledger, will provide the material that eventually makes up the foundation of a business’s financial statements. This includes expense reports, cash flow and salary and company investments. The accounting equation is based on the premise that the sum of a company’s assets is equal to its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
What is the basic accounting equation formula?
For every transaction, both sides of this equation must have an equal net effect. Below are some examples of transactions and how they affect the accounting equation. For example, if a company becomes bankrupt, its assets are sold and these funds are used to settle its debts first. Only after debts are settled are shareholders entitled to any of the company’s assets to attempt to recover their investment.
To build a stronghold on accounting and indulge in higher studies relating to accounts, you need to grasp the methods right from their grassroots. Now say after 2 years, you want to expand the business but do not have funds. So you go to a bank and get a loan of another $10,000 to expand the operations.
Want More Helpful Articles About Running a Business?
If you’re a small business owner who would prefer to monitor your company’s cash flow statement with your own two eyes, there are financial accounting formulas that you should be familiar with. These basic accounting equations are rather broad, meaning they can apply to a variety of businesses. Since every business transaction affects at least two of a company’s accounts, the accounting equation will always be “in balance”, meaning the left side of its balance sheet should always equal the right side. Thus, the accounting formula essentially shows that what the firm owns (its assets) has been purchased with equity and/or liabilities. Individual transactions which result in income and expenses being recorded will ultimately result in a profit or loss for the period. The term capital includes the capital introduced by the business owner plus or minus any profits or losses made by the business.
The accounting equation states that a company’s total assets are equal to the sum of its liabilities and its shareholders’ equity. Below, we’ll cover the fundamentals of the accounting equation and the top business formulas that businesses should know. Read end-to-end for a thorough understanding of accounting formulas or use the list to jump to an equation of your choice. The accounting equation summarizes the essential nature of double-entry system of accounting. Under which, the debit always equal to credit, and assets always equal to the sum of equities and liabilities.
Accounting ratios come with wide-reaching use and necessity, even for those of us who are not accountants. Many of us like to invest money that we look at as long- or short-term opportunities. A savvy investor knows how to use accounting ratios to determine whether a stock presents a lucrative opportunity or perhaps a liability that other investors have yet to realize.
To begin with, it doesn’t provide an analysis of how the business is operating. Furthermore, it doesn’t totally keep accounting mistakes from being made. In any event, when the balance sheet report adjusts itself, there is still a chance of a mistake that doesn’t include the accounting equation.
Every transaction is recorded twice so that the debit is balanced by a credit. Knowing how to calculate retained earnings helps business owners to perform a more in-depth financial analysis. Also, the statement of retained earnings allows owners to analyze net income after accounting for dividend payouts. Owners should calculate the statement of retained earnings at the end of each accounting period, even if the amount of dividends issued was zero. All basic accounting formulas discussed throughout this post highlight the importance of double-entry bookkeeping. An accounting transaction is a business activity or event that causes a measurable change in the accounting equation.


















